
This chapter describes IBM's ASRT LAN Network Manager (LNM). It includes the following sections:
Use LNM to manage token-ring networks interconnected by source route bridges. It lets you monitor the operation of rings, bridges, and individual ring stations.
Information collected by software agents on the bridge is available to LNM management stations. More specifically, LNM agents forward collected information via another agent called the LAN Reporting Mechanism (LRM), a proprietary IBM protocol. Information forwarding is done via an LLC2 connection to a LAN Network Manager station.
The LNM agents and their functions include:
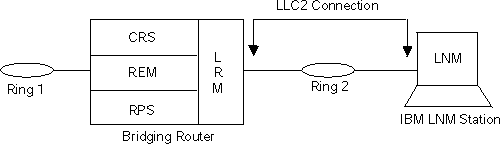
Figure 25 illustrates the connection between the IBM bridge, LNM agents, and the IBM LNM station.
Figure 25. LNM Station and Agents

LLC2 Connection
*-------------------*
*----------------*---*| |
| CRS | || |
*----------------* L |V V*----*
Ring 1 *-* REM | R *------* Ring 2 *-----*LNM |
*----------------* M | *----*
| RPS | | IBM LNM Station
*----------------*---*
Bridging Router
The following sections describe each LNM agent in more detail.
At the request of LNM, CRS obtains and forwards ring station status to LNM. Use CRS to set ring station parameters and remove a station from the ring.
Configuration information generated by ring stations is forwarded to LNM. When LNM requests the status of a ring station, CRS builds and sends MAC frames to the station to obtain the information. CRS then sends the following frames to the ring station:
When the ring station replies, CRS puts the information into a properly formatted LLC2 frame and forwards it to LNM.
CRS can also remove a ring station from the ring at the request of LNM. To remove a ring station, CRS sends a Remove Station MAC frame to the ring. CRS also returns a response to LNM indicating the success or failure of the removal.
When CRS receives a Report New Active Monitor MAC frame, it forwards the information to LNM. When a Report NAUN (Next Active Upstream Neighbor) Change MAC frame is received, this information is also reported. The CRS agent has its own functional address that ring station MAC layers can use to forward MAC frames to CRS.
RPS inserts ring stations onto the ring. When a ring station is newly inserted into the ring the following occurs:
The RPS function has an associated functional address for receiving the MAC frames that other ring stations send to it.
| Attention: | When a station attempts to insert into a ring, it sends a Request
Initialization MAC frame to the Ring Parameter Server (RPS) for that
ring. If this frame is copied successfully by the RPS, then the station
expects to receive an Initialize Ring Station MAC frame back from the
RPS. If no such frame is received, the station will not insert into the
ring.
A station may fail to insert into the ring if the device is configured for LNM, becomes the Ring Parameter Server, and enters a congested state that prevents the sending of the Initialize Ring Station MAC frame. The solution to this problem is to disable RPS on the affected port. If RPS is not enabled and no server copies the Request Initialization frame, the sending station does not expect a response and it will insert into the ring. |
REM observes the operation of the attached token-ring by looking for hard errors and soft errors. It then reports these to the LRM and aids in isolating the cause of the errors. It does the following during hard error detection:
REM monitors soft errors as follows:
LRM controls the connection of LNM to the agents. LRM establishes reporting links between itself and each connected LNM. A reporting link is an LLC2 connection between LNM and LRM.
All communication between LNM and the agents is done via a reporting link. LRM passes management data to and from the appropriate agents to the reporting links. Up to four reporting links are supported. One is designated the controlling link and the other three are designated as observing links.
An LNM connected via the controlling link can perform all available operations. LNMs connected by observing links can perform only a limited subset of the available operations.
IBM 2212 supports multi-port Token-Ring and two Token-Ring configurations.
The LNM agent and the LNM station always assume that messages are being passed on a two-party model. LNM is enabled, however, on a per-bridge port basis to be consistent with the existing configuration.
In a multi-port configuration, LNM can be enabled on any source-routing token-ring bridge port. An instance of LNM is created for each port upon which LNM is enabled.
In a two token-ring configuration, the other port is always designated by a pseudo address. This is known as a multi-port bridge. It can correspond to a virtual ring or a serial line interface.
Only in the case where the IBM 2212 bridge has two source routing token-ring ports is the other port in the two-port model bridge a token-ring with a real address.
To obtain the MAC addresses needed to configure the LNM Manager, enter list lnm ports at the ASRT> prompt.
The LAN Bridge Server (LBS) can report packets-forwarded and packets-discarded performance data statistics when requested by the manager station. Remote configuration updates from the manager station are not supported.
In LANs, the data link layer comprises two sublayers: the medium access control (MAC) and the link layer control (LLC). LLC provides two types of service:
LAN Network Manager (LNM) requires LLC2 connection-oriented services. LLC2 provides capabilities for:
The LLC sublayer conforms to the IEEE 802.5 standard.